
2021级博士生潘园的论文在Appl.Catal.B Environ.刊出

第一作者:潘园(湖南大学博士生)
通讯作者:刘智峰 教授(湖南大学)
论文DOI:10.1016/j.apcatb.2025.125420
图文摘要
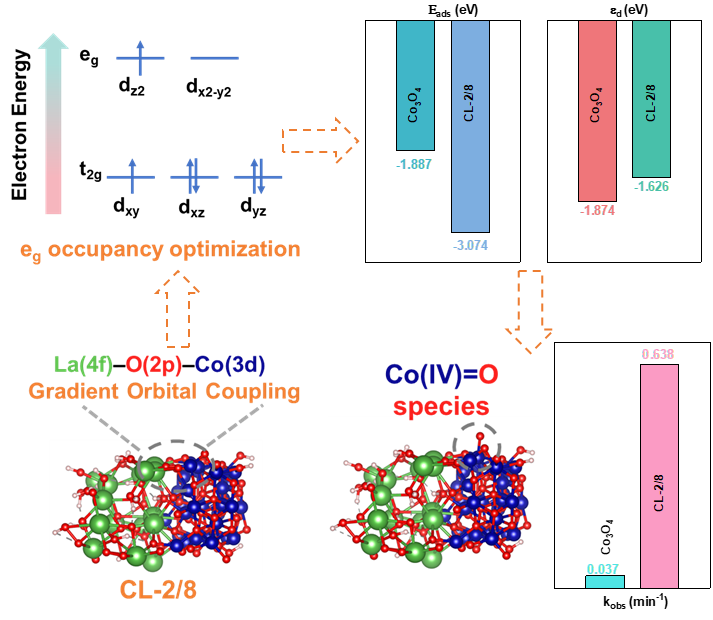
成果简介
近日,湖南大学环境科学与工程学院刘智峰课题组在Applied Catalysis B: Environment and Energy上发表了题为“Optimized the eg Occupancy of Co Active Site through 4f–2p–3d Gradient Orbital Coupling for Efficient Fenton-like Catalysis”的研究论文(10.1016/j.apcatb.2025.125420),探究了具有4f–2p–3d梯度轨道耦合异质界面催化剂在过一硫酸氢盐(PMS)活化过程中调控活性位点电子结构和活性物种选择性生成的机制。通过材料表征、淬灭实验、EPR光谱和DFT计算研究了MOF衍生的具有梯度轨道杂化La-O-Co单元的CoLaOx-HC催化剂(CL-2/8)在活化PMS降解卡马西平过程中Co位点eg占据调控的关键作用。在该体系中,Co(IV)=O的选择性生成几乎达到100%(产率:3.345 × 10−10 M),kobs达到0.638 min-1,比CL-10/0(Co3O4)提高了17.2倍。机理研究表明,梯度轨道耦合精确调节了La-O-Co界面的电子排列,增加了Co 3d轨道eg占据,从而促进了PMS吸附和Bader电荷转移,减小了Co(IV)=O生成的能垒,从而高效选择性生成Co(IV)=O。这项工作提出了一种有效的微污染物去除工艺,并为研究调控活性位点本征电子结构介导活性物种选择性生成提供了新的见解。
全文速览
本工作以溶剂热法制备双金属MOF前体并煅烧制备了CoLaOx-HC催化剂,用于活化PMS降解卡马西平。淬灭实验、探针实验、EPR光谱和原位Raman光谱证实了CL-2/8/PMS体系生成Co(IV)=O物种主导污染物去除。通过计算吸附能、吉布斯自由能和态密度,发现活性Co位点增强的eg占据有效促进了PMS吸附,改变速率决定步骤并降低Co(IV)=O生成能垒,实现Co(IV)=O选择性生成和污染物的高效降解。
引言
多价过渡金属非均相催化剂,特别是具有独特的d轨道电子结构和特定氧化还原电位的钴(Co)基尖晶石氧化物,被认为是用于水净化的最有效的PMS活化剂之一。相比传统自由基体系,非自由基氧化途径,特别是高价金属-氧物种,由于具有更高的氧化还原电位(> 1.95 VNHE)、选择性、稳态浓度(~10-8 M)和更长寿命(通常为几秒),并且氧化剂利用率高,因此更适合于复杂环境基质中的水净化。然而,在PMS活化过程中较大的能量屏障使Co(IV)=O物种有效选择性生成仍然具有挑战性,相关研究报道仍然很少。因此,本工作通过构筑4f–2p–3d梯度轨道耦合异质界面调控了Co位点的本征电子结构(eg占据),并通过淬灭实验、探针实验、EPR表征和理论计算等手段深入研究了优化的Co位点eg占据在调控活性物种生成和增强催化性能中的主导机制。
图文导读
催化剂制备和表征
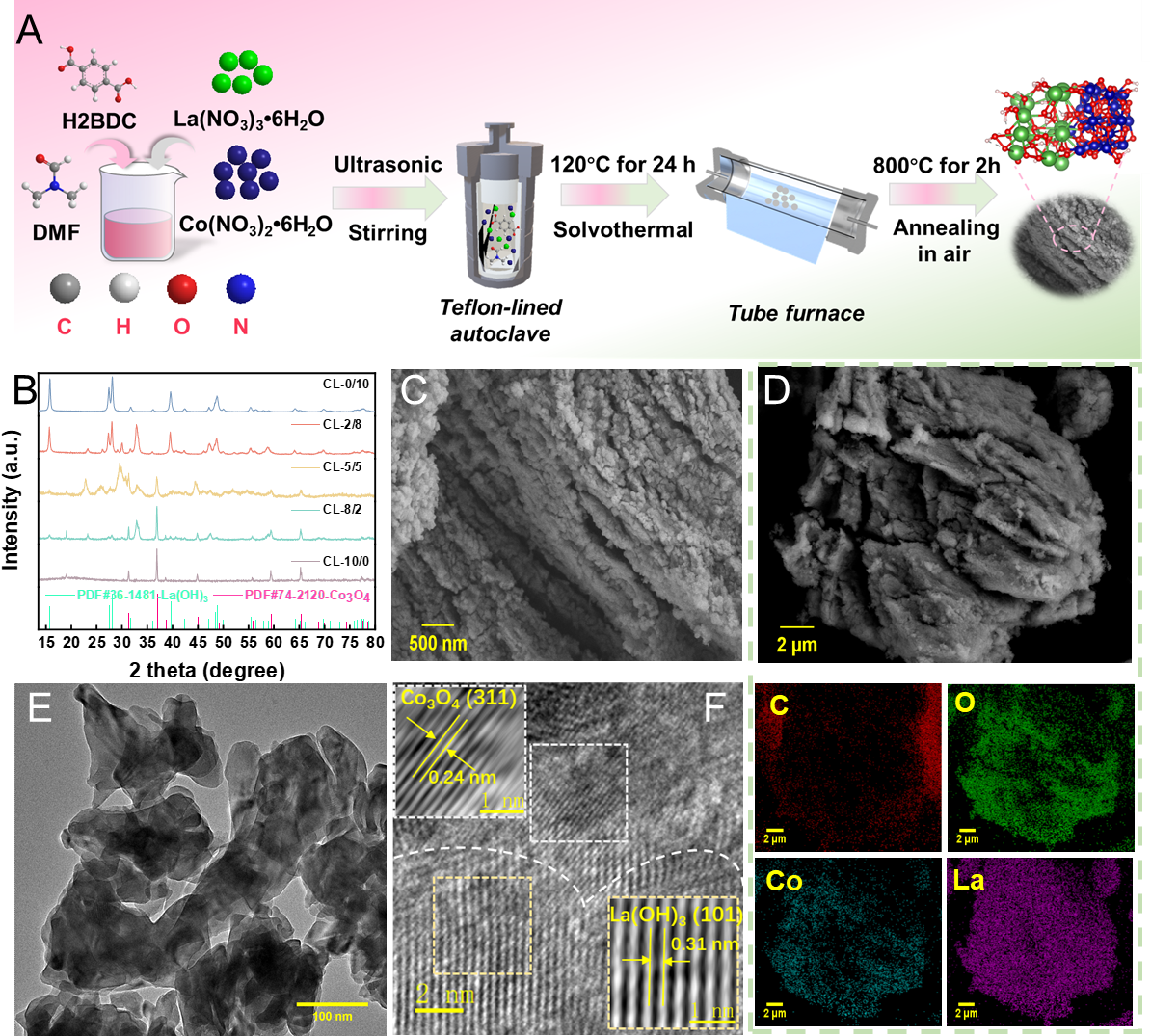
Figure 1. (A) Schematic illustration of the synthesis process for CL-2/8 sample. (B) XRD patterns of the as-prepared samples. (C) SEM image of CL-2/8 sample and (D) the corresponding EDS elemental mapping images. (E, F) The TEM and HRTEM images of CL-2/8 sample. Copyright 2025, Elsevier Inc.
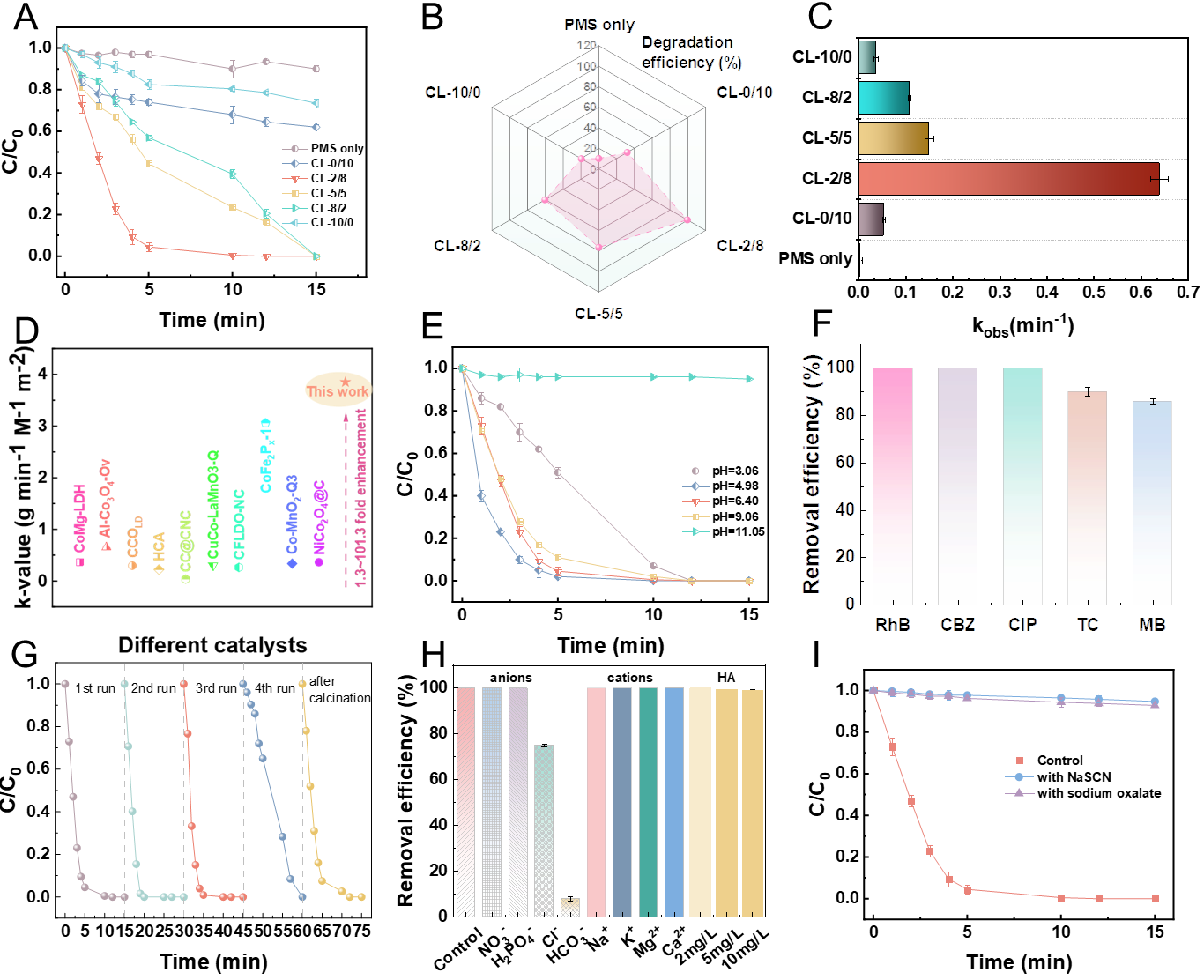
Figure 2. (A) Nitrogen adsorption-desorption isotherms of as-prepared catalysts. XPS characterizations of CL-2/8 sample: (B) high-resolution XPS for C 1s spectra, (C) O 1s spectra, (D) La 3d spectra and (E) Co 2p spectra. (F) The calculated charge density difference (Top view) of CL-2/8 heterostructure catalyst. (The yellow region represents the electron accumulation, while the cyan region represents the electrons depletion.) (G) The curve of fitted susceptibility versus. temperature based on Curie–Weiss law. (H) The representative EELS spectra of the Co3O4 and CL-2/8 samples at O K-edge. (I) The orbital interactions between cobalt cations in different spin state and the -OH species. The bond order (BO) was also shown in this Figure. The BO is defined as half the difference between the number of bonding electrons and the number of antibonding electrons. Copyright 2025, Elsevier Inc.
以对苯二甲酸有机配体和金属硝酸盐作为原料溶剂热法制备CoLa-MOF前驱体,经高温煅烧衍生CoLaOx-HC催化剂。材料表征表明,催化剂呈现Co3O4/La(OH)3异质界面结构,La-O-Co单元的构建促进了界面电子传递,优化了活性Co位点3d轨道的eg占据。
性能测试

Figure 3. (A) The degradation process of CBZ in different catalysts-activated PMS systems and (B) the corresponding degradation efficiency for CBZ after 10 min reaction. (C) The observed kinetic rate constants (kobs) of CBZ in as-prepared catalysts activated PMS systems. (D) Kinetics comparison of organic micropollutants (OMPs) degradation by CL-2/8 catalyst and other Co-based catalyst/PMS systems. (E) Influence of pH value on CBZ elimination. (F) Removal of various OMPs in the CL-2/8/PMS system after 15 min reactions. (G) CBZ abatement in four consecutive cycles in the CL-2/8/PMS system. (H) Effect of coexisting background inorganic ions and natural organic matter (i.e. HA) on CBZ removal. (I) Influence of NaSCN (5 mM) and sodium oxalate (5 mM) on CBZ degradation. Reaction conditions: [catalyst] = 0.1 g L-1, [PMS]0 = 1 mM, [pollutants]0 = 10 mg L-1, [anions] = 0.01 M, initial solution pH = 6.4, T = 298 K. Copyright 2025, Elsevier Inc.
CL-2/8/PMS体系具有良好的污染物去除性能,在15分钟内实现CBZ的完全去除,归一化速率常数在Co基非均相催化剂中表现突出,且表现出优异的环境适应性和实际应用潜力。
活性物种鉴别和定量分析
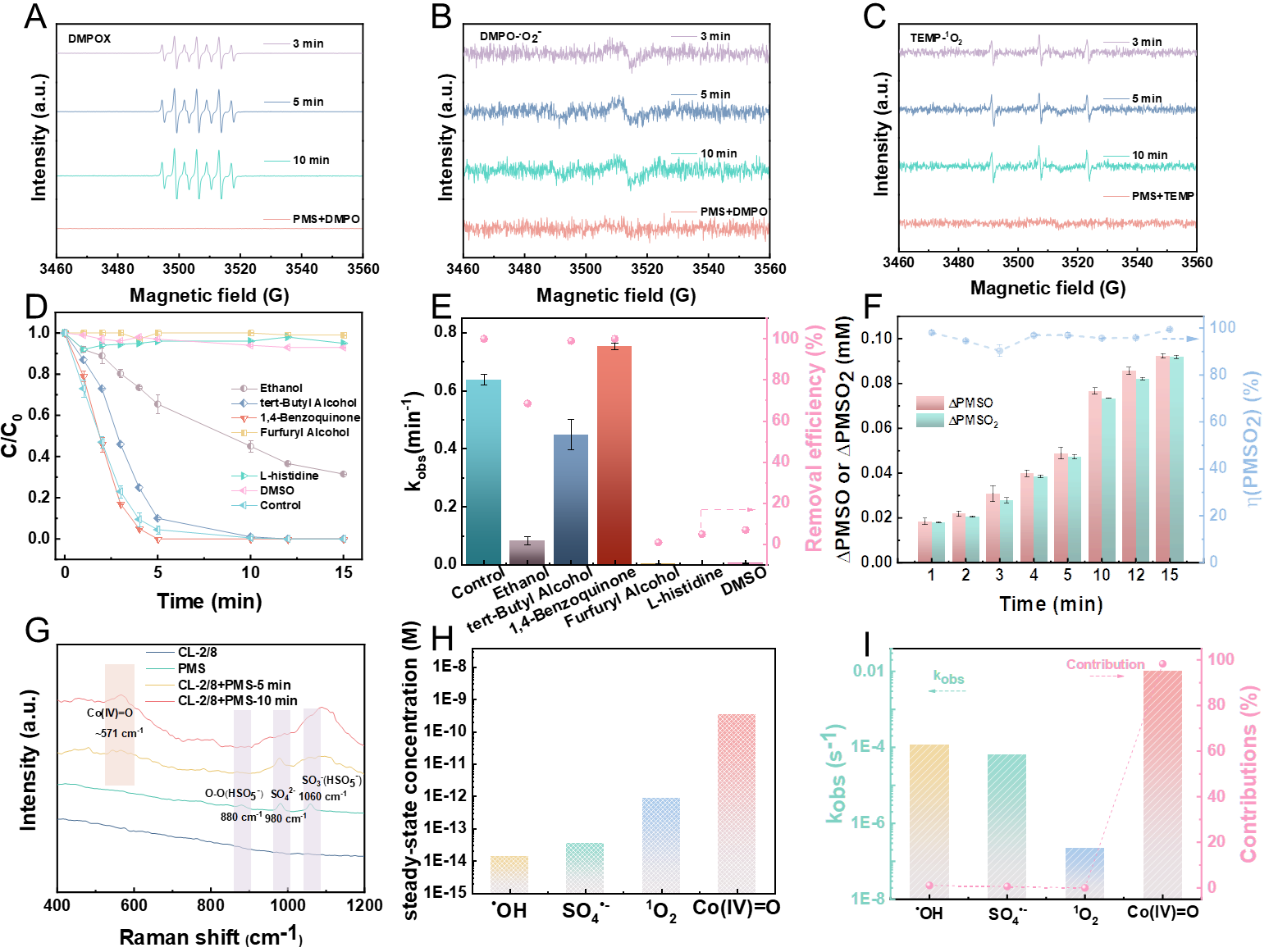
Figure 4. Experimental EPR spectra for (A) •OH/SO4•− and (B) •O2− in the presence of DMPO, (C) EPR spectra for 1O2 in the presence of TEMP in various systems with different reaction times. (D) Quenching experiments of the CL-2/8/PMS system and (E) the corresponding kinetic rate constants and degradation efficiency. (F) the corresponding transformation rate of PMSO in the CL-2/8/PMS system and (G) In situ Raman spectra of the CL-2/8/PMS system. (H) Steady-state concentrations and (I) observed reaction kinetic rate constants and oxidation contributions of different reactive species to CBZ abatement in the CL-2/8/PMS system. Reaction conditions: [catalyst] = 0.1 g L-1, [PMS]0 = 1 mM, [CBZ]0 = 10 mg L-1, [PMSO] = 0.5 mM, initial solution pH = 6.4, T = 298 K. Copyright 2025, Elsevier Inc.
淬灭实验、原位EPR测试、原位Raman光谱和基于探针化合物定量实验表明Co(IV)=O是CL-2/8/PMS体系的主要活性物种,稳态浓度达3.345×10−10 M,Co(IV)=O对该催化过程的总kobs贡献约为98.28%。
机制研究
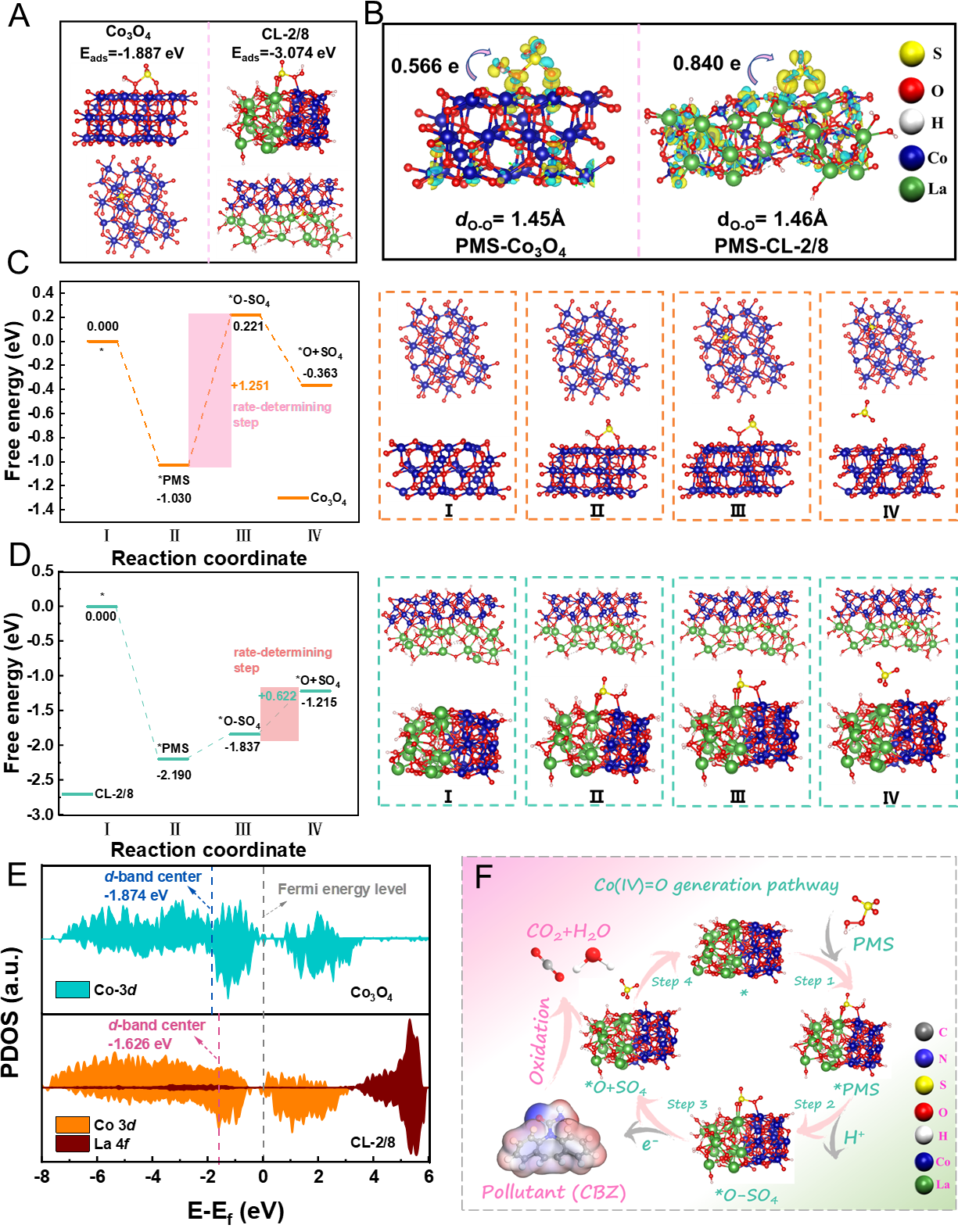
Figure 5. Theoretical calculations of PMS adsorption and activation on Co3O4 and CL-2/8 catalysts. (A) The adsorption energies of PMS on Co3O4 and CL-2/8 surface active sites. (B) Charge-density differences of PMS absorbed on Co3O4 and CL-2/8 (blue and yellow contours correspond to electron deletion and accumulation, respectively). Energy profiles of the reaction pathways for Co(IV)=O generation on (C) Co3O4 and (D) CL-2/8 by PMS activation. The asterisk (*) denotes the adsorption site. (E) Partial density of states (PDOS) of Co 3d in Co3O4 and CL-2/8. (F) Proposed mechanism of Co(IV)=O selective formation in the CL-2/8/PMS system for superior Fenton-like reaction. Copyright 2025, Elsevier Inc.
相比于Co3O4催化剂,CL-2/8活性Co位点增强的eg占据提高了与O 2p轨道的键序,进而对PMS的吸附更强,促进了更多的电子转移。CL-2/8/PMS生成Co(IV)=O物种的能垒更低。态密度(DOS)分析表明,La-O-Co单元通过O桥实现了轨道之间的耦合,优化了Co位点的电子结构,特别是eg占据。梯度轨道杂化调控了催化剂的d带中心,使其更靠近费米能级,增强了对反应物的吸附作用(更高的键序和吸附能)和活化(更低的反应能垒),进而实现了Co(IV)=O物种的选择性生成。
污染物降解路径
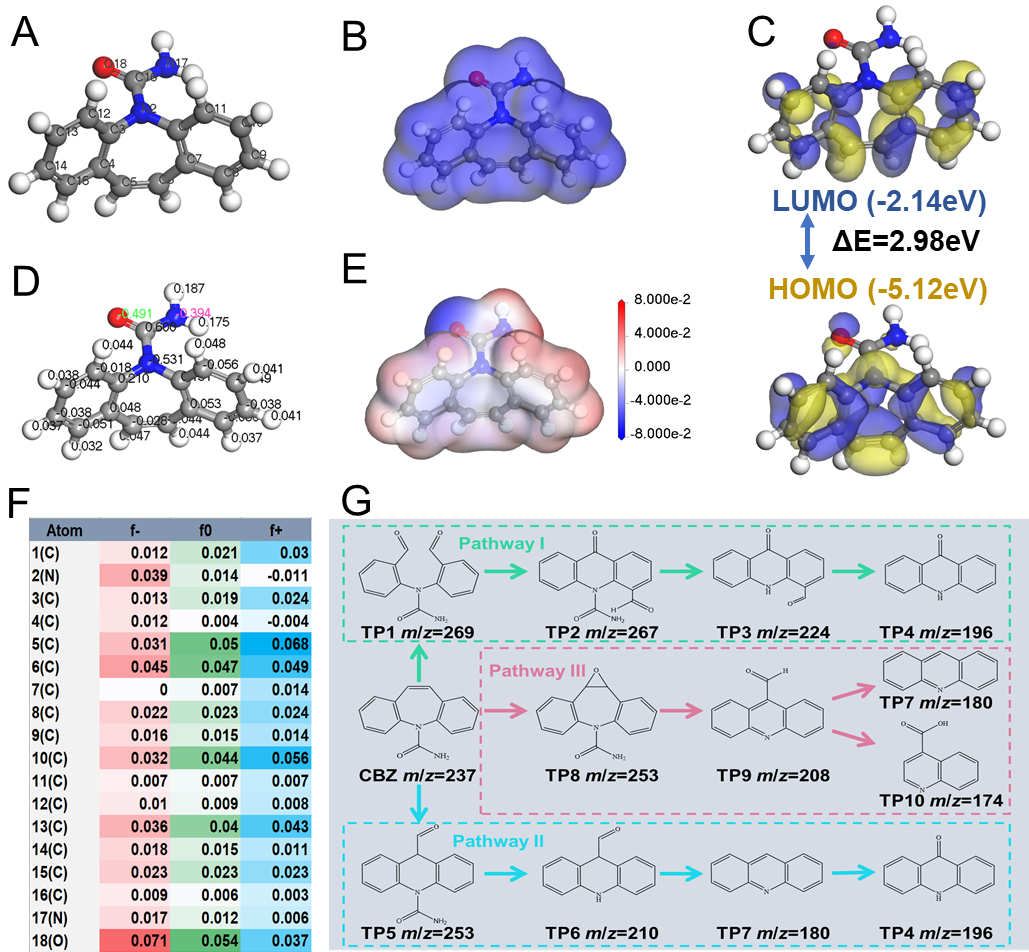
Figure 6. (A) The optimized geometric structure, (B) electron density distributions, (C) HOMO and LUMO orbitals, (D) charge distribution of each atom and (E) electrostatic potential mapping of CBZ molecule. (F) Fukui index of CBZ. (G) The proposed degradation pathways of CBZ elimination process in the CL-2/8/PMS system. Copyright 2025, Elsevier Inc.
基于DFT和福井函数的理论计算,研究了CBZ的分子结构、潜在活性位点、HOMO-LUMO前线轨道分析、静电势。结合HPLC-MS结果提出了3种可能降解路径,并使用毒性估计软件工具(ECOSAR和T.E.S.T.)评估CBZ及其中间产物的生态毒性。
小结
本研究提出了一种梯度4f−2p−3d轨道耦合策略来合成具有不对称La-O-Co异质结构界面的CoLaOx-HC催化剂(CL-2/8),通过激活PMS选择性形成Co(IV)=O来去除难降解有机污染物。结构表征和系列实验结果以及DFT计算证明了稀土元素La通过O桥接实现梯度轨道杂化,调控了活性Co位点的3d轨道的eg电子占据,使得与PMS之间形成更强的键序,增强了PMS的吸附和催化剂之间的电子转移过程,最终优化了速率决定步骤并降低生成Co(IV)=O物种的能垒,实现污染物的高效和稳定降解。本工作中提出的CL-2/8/PMS体系是一种有效的有机污染物降解过程,为高效激活PMS催化剂的设计和实现活性物种的选择性生成提供了新的见解。
- 附件【2025-潘园-ACB.pdf】已下载次
【关闭】
