
2022级硕士蓝宸睿的论文在Chemical Engineering Journal刊出

第一作者:蓝宸睿 2022级硕士生
通讯作者:汤琳教授、冯浩朋助理教授
论文DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2025.171769
图文摘要
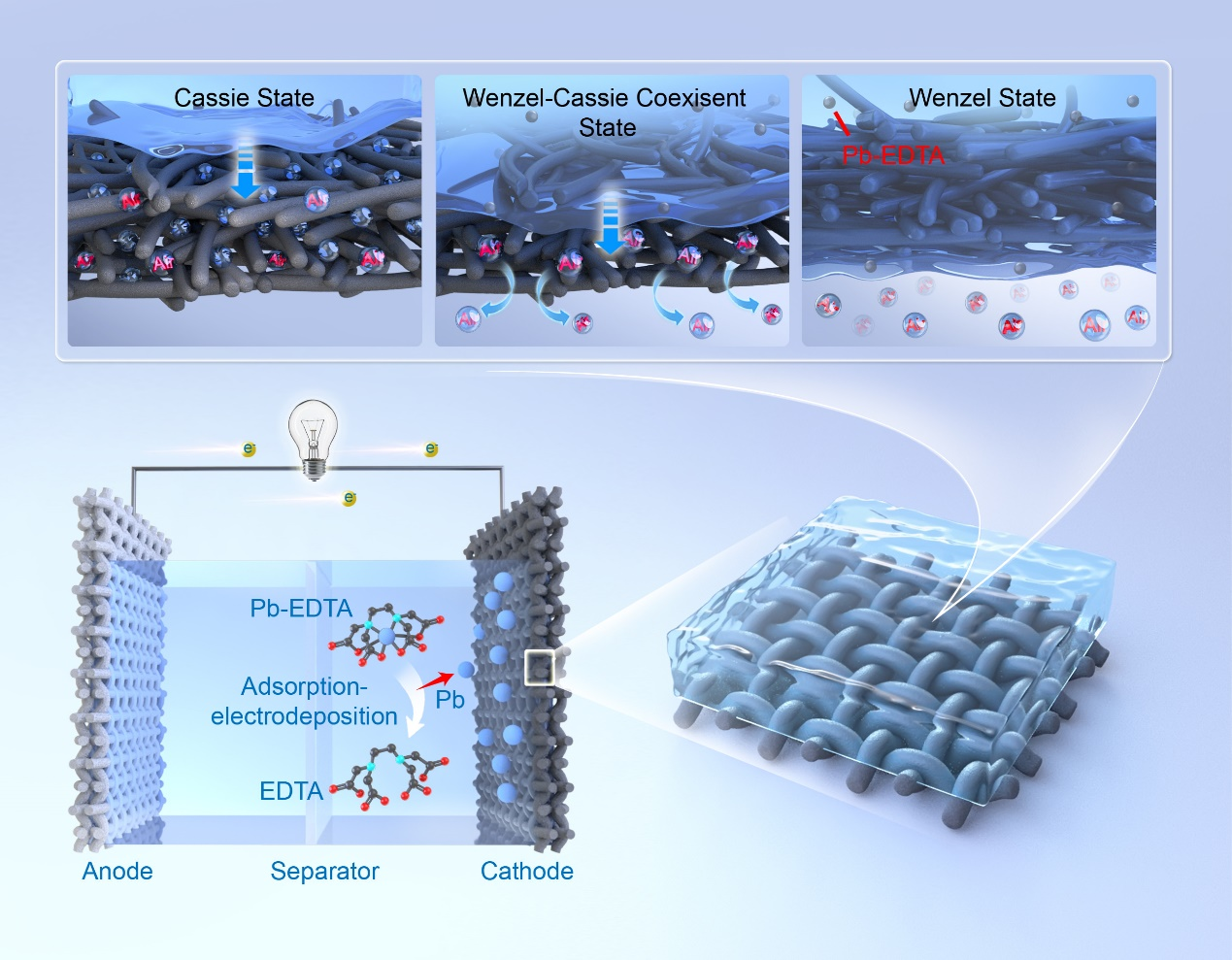
成果简介
近日,湖南大学环境科学与工程学院汤琳教授课题组在Chemical Engineering Journal上发表了题为“Regulating electrode wettability by construction of the liquid-liquid interface for improving metal electrodeposition performance”的研究论文(10.1016/j.cej.2025.171769)。该研究针对电沉积去除重金属有机络合物废水中电极材料的效率低、成本高等问题,提出了一种结合液滴冲击和电润湿效应的物理改性方法,以实现对廉价碳毡电极界面性能的可逆调节。结果表明,该电极的电沉积反应速率提高了~100倍,并且在连续工作100小时以上仍保持优越的稳定性。该策略还将电沉积修复重金属污染废水的技术成本从~1400元降低到~30元。本研究结果表明,构建的液-液界面可以增强电解质离子扩散,增加离子可达表面积,降低电极界面阻抗,显著提高传质效率。该研究为液-液界面在废水中重金属有机络合物电沉积过程中的关键作用提供了基本见解,这可能为未来先进电极系统的设计提供新的概念。
全文速览
本研究通过结合液滴冲击和电润湿效应的物理改性方法,实现对Pb-EDTA的解络,同时实现Pb离子的去除以及EDTA的回收。深入解析构建合适的液-液界面对电沉积性能提升的机制,同时在实际应用实验中展示出优异性能。该成果为未来电化学体系电极设计提出新思路,具有良好的工业应用前景与推广潜力。
图文导读
一、构建液-液界面调节电极润湿性状态
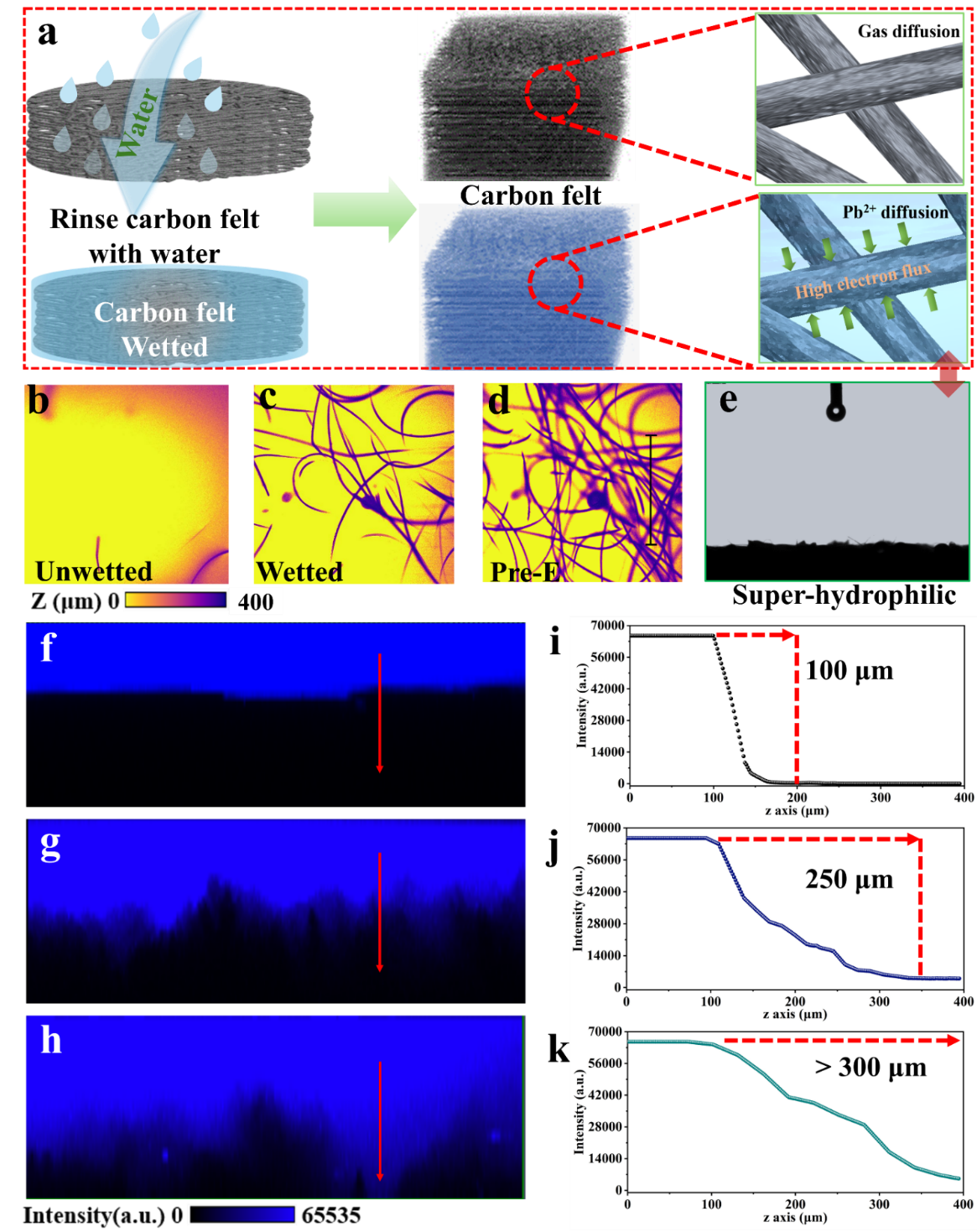
Fig. 1 (a) Schematic diagram of wetted CF by rinsing with water and wetting states of pristine and wetted CF electrodes. (b-d) Confocal 3D reconstruction images of unwetted, wetted, and pre-E CF electrodes. (e) Contact angle measurement of wetted CF. (f-h) Cross-sectional fluorescence images scanned from labeled regions in (b-d), scale bar: 10 μm. (i-k) From top to bottom are unwetted, wetted, and pre-E CF electrodes. Corresponding z-axis fluorescence intensity line scans of labeled regions (red arrows) in (f-h).
液-液界面结构可以改变碳毡电极的电解质润湿状态,电解质渗透深度会随着电极润湿性的增加而增加。构建合适的液-液界面结构能降低电解质液体进入电极内部的能量势垒,加快离子扩散速度,提高电子传递效率。
二、液-液界面提高电极的电沉积效率
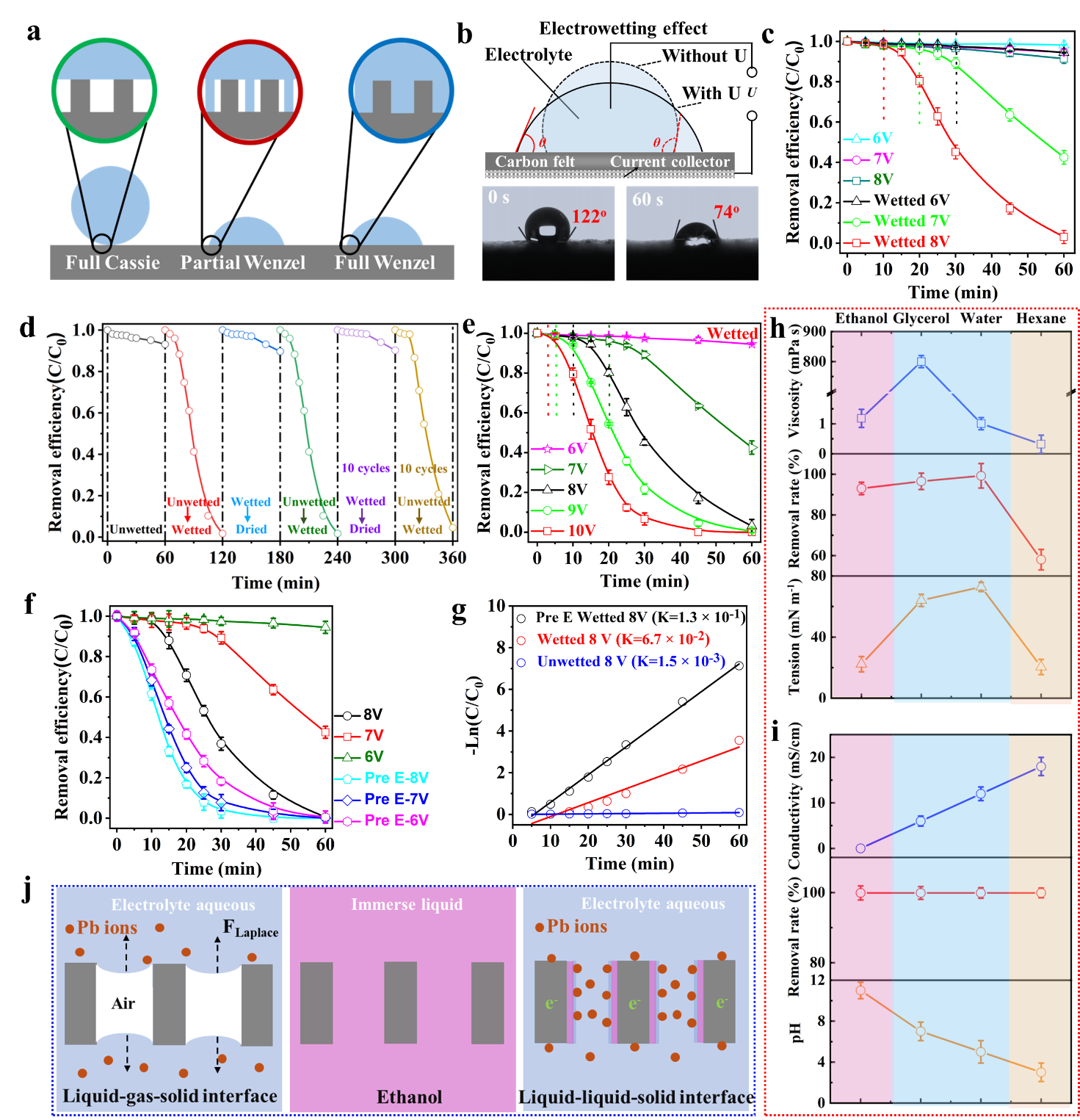
Fig. 2 (a) Schematic of the contact situation between the electrode substrate and the electrolyte liquid under different wetting states. (b) Schematic of the electrowetting effect, and corresponding changes in contact angle. (c) Pb electrodeposition performance of unwetted and wetted CF electrodes at an initial pH of 3.0. (d) The stability and reproducibility of the liquid-liquid interface test. (e) Pb electrodeposition performance of wetted CF electrodes with different operating voltages. (f) Pb electrodeposition performance of the wetted CF electrode after the Pre-E process at 10V voltage and related electrodeposition rate (g). (h) Influence of interfacial liquid properties on the Pb electrodeposition performance. (i) The influence of pH and conductivity of the interface aqueous solution on electrodeposition performance. (j) Schematic diagram of the effect of interfacial fluid ethanol on the electrodeposited of lead ions process.
在完全Wenzel状态下的碳毡电极,展示出最优异的电沉积性能,金属沉积速率分别约为Cassie和部分Wenzel状态下电极的100倍和2倍;电化学活性面积分别约为Cassie和部分Wenzel状态下的6倍和1.2倍。证明构建合适的液-液界面能显著提升电沉积性能。
三、液-液界面结构提升电极润湿性和电沉积效率的机制分析
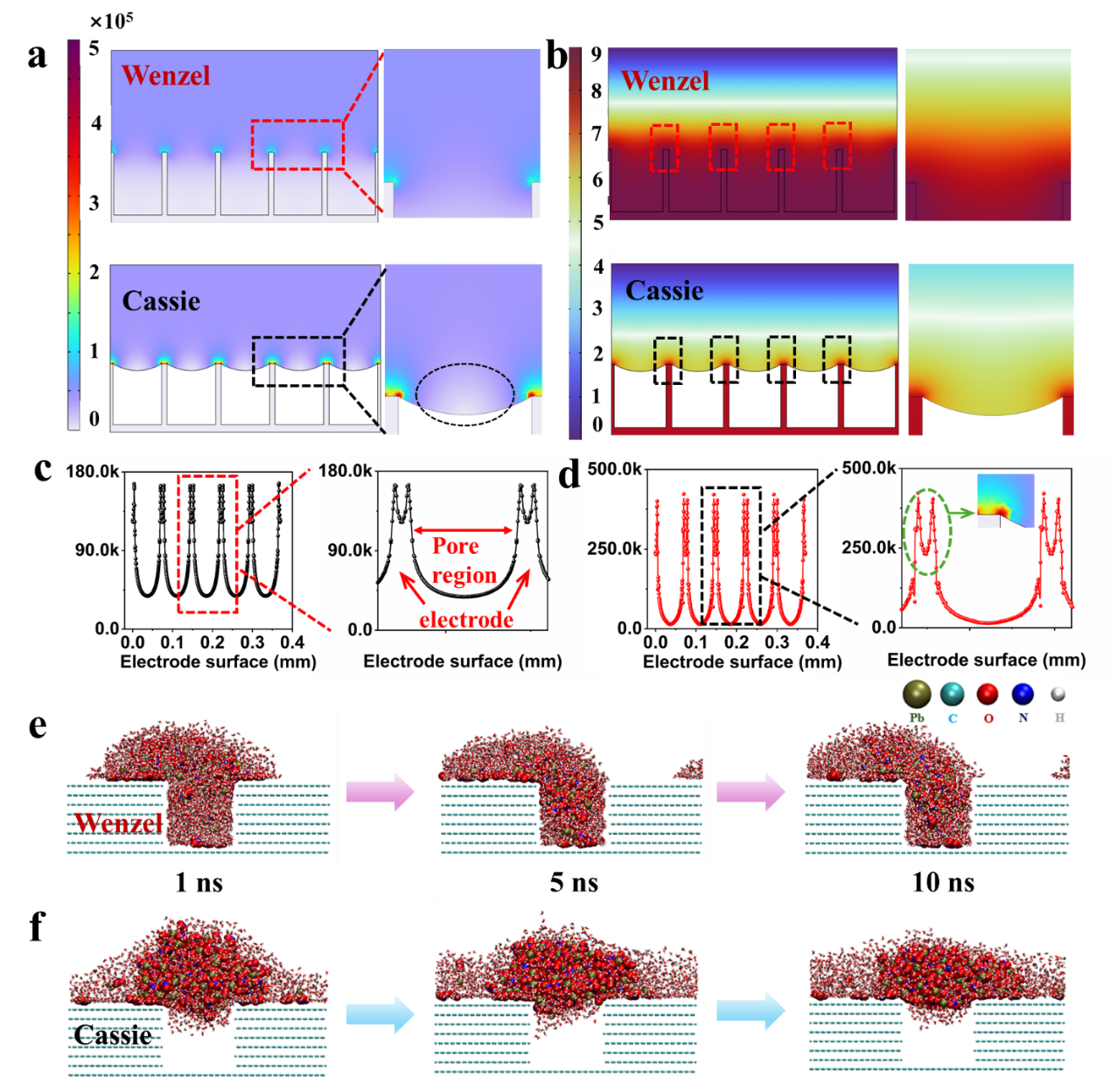
Fig. 3 (a) COMSOL simulation of the electric field distribution at the interface between the electrode and electrolyte under different wettability states. (b) The electric potential distribution in the electrolyte near the electrode surface varies with wettability states. Quantitative electric field strength at the pore and electrode-electrolyte region, (c) Wenzel state; (d) Cassie state. (e-f) MD simulation of the permeation process of Pb2+ under an electric field at different wettability states.
模拟电场分布表明,由于电解液无法进入Cassie状态下电极的内部,所以在Cassie状态下,电极孔隙内不存在电场;而Wenzel状态下,电场均匀分布在电极的孔隙内外;分子动力学模拟表明,Wenzel状态下,电解液中的金属离子可以迅速迁移至电极孔隙内;而在Cassie状态下,电解质溶液很难进入孔隙内部。这表面,构建合适的液-液界面结构可以通过加速电极与电解液之间的传质效率来改善金属电沉积性能。
小结
本研究提出一种结合液滴冲击结合电润湿效应的物理改性方法,实现对金属电沉积效率的显著提升。研究揭示了构建合适的液-液界面结构可以改善电极润湿性,降低电解质进入电极的能量势垒,加速电极与电解质溶液之间的传质效率,从而显著改善金属电沉积性能。该策略解决了传统电极材料效率低、成本高等问题,为未来电极系统的设计提供了新思路。
【关闭】
